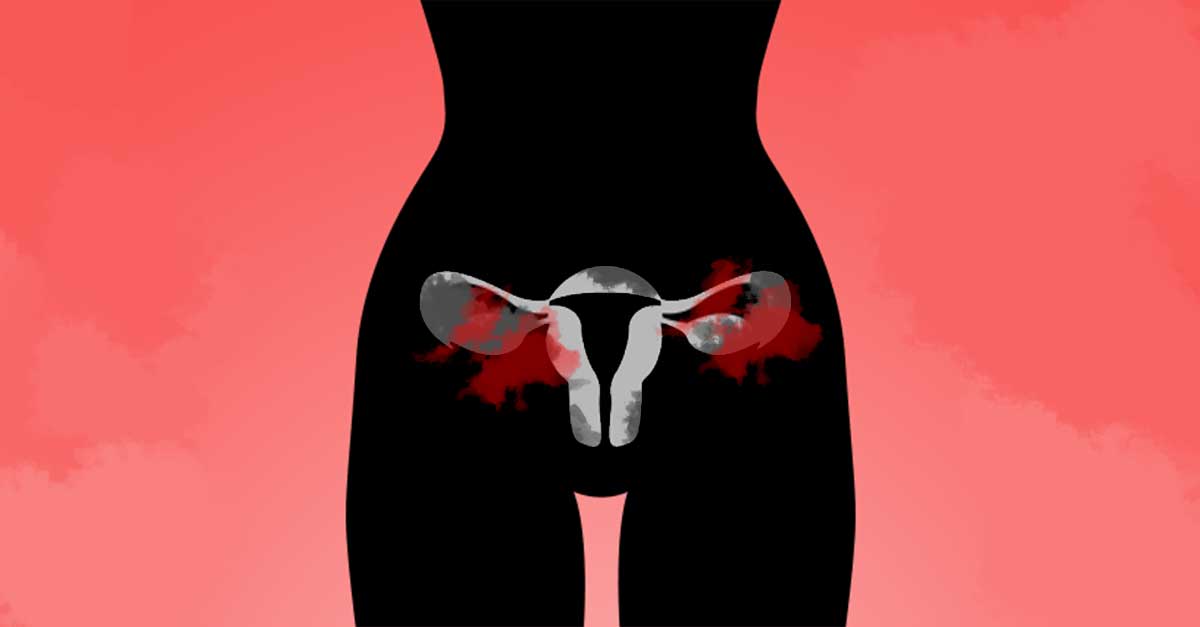
According to the National Cancer Institute, ovarian cancer accounts for only around 3% of all cancers in women, but it is still the fifth leading cause of cancer-related death among women in the United States. Among deaths caused by cancer in the female reproductive system, ovarian cancer ranks the highest.
Despite being uncommon, the high mortality rate has been attributed to two main causes: a lack of both early symptoms and effective screening tests.1Ovarian cancer is notorious for not being detected in cervical screening tests.2
Silent Killer Or Wicked Whisperer?
Numerous articles will tell you that ovarian cancer is a “silent killer,” a symptomless disease that can only be detected when it is too late to recover. However, according to scientific research, ovarian cancer “can” be detected early. Contrary to popular belief, it might be a disease that gives out early signals, just more in “whispers.”3
What makes these signs difficult to decipher is that the same symptoms are often caused by common ailments such as gastrointestinal problems, bladder infections, and irritable bowel syndrome.
In fact, studies suggest that nearly half of women will develop symptoms at least three months before diagnosis. However, these symptoms are often so vague that it may not even seem like they are related to any gynecological issues.4 Almost 94% of women have lived longer than five years after diagnosis when ovarian cancer was detected early.5 This means being vigilant is vital.
Early Signs And Symptoms
Let us take a look at some symptoms to watch out for:
Abdominal Pain
Persistent pain in the stomach or pelvis is one of the major symptoms of ovarian cancer.
Bloating
Bloating can typically occur due to indigestion or PMS. But do not take it lightly if that feeling does not go away. If bloating around the abdomen persists for more than three weeks, or your clothes do not fit around the waist anymore, see a doctor immediately.6
Weight Loss
One of the most common, and often the first noticeable signs of cancer, is weight loss. At the time of diagnosis, nearly 40% of people with cancer report unexplained weight loss.
This could be due to several reasons, such as changes in the immune system, loss of appetite, constipation, or even pain due to cancer.7
Feeling Full Without Having Eaten Much
Known in medical terms as “early satiety,” this is the inability to eat a normal-sized meal. It could be because you either feel full after eating very little or feel nauseated while attempting to eat the amount you regularly consume.
This is usually a common symptom associated with a number of other conditions such as GERD, peptic ulcers, or obstruction in the bowel.8
Needing To Urinate Frequently
This is often misdiagnosed as urinary tract infection. But if an infection has not been spotted and the symptoms persist, see an OB/GYN immediately.
Changes
In Bowel Habits
With constipation, the stool tends to be dry and hard, making it difficult to pass. Bowel movements also happen infrequently. This common sign of cancer is often linked to tumors in the abdomen.9
Other symptoms important to watch out for include: extreme fatigue, pain during sex, lower back pain, and menstrual irregularities.
It cannot be stressed enough that just the presence of these symptoms do not mean you have ovarian cancer. However, see an OB/GYN at the earliest if these symptoms are:
- New: They are not normal for you or you have noticed them recently, within the last year.
- Frequent: They occur for more than 12 days a month.
- Persistent: They do not go away.10
Risk Factors
While there is currently no way to predict if someone will get ovarian cancer, women with certain genetic makeup, hereditary factors, or medical conditions are more susceptible.1112
Genetic Factors
- Breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) and breast cancer gene 2 (BRCA2) are responsible for about 10–15% of all ovarian cancers.
- Women with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), another inherited syndrome (more commonly known as Lynch syndrome), have about a 12% lifetime risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Women with hereditary breast-ovary cancer syndrome have a risk of 10–44%.
Family History
Family history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, colon cancer, and uterine cancer is linked to a higher risk of ovarian cancer. The lifetime risk of a woman who has an immediate relative with ovarian cancer is 5%, while that of an average woman’s lifetime is 1.4%.
Increasing Age
Ovarian cancer rates are highest in women aged 55–64 years and are typical of perimenopausal and postmenopausal women. The frequency only increases with age.
Reproductive History And Infertility
Risk of getting ovarian cancer seems to be connected to menstrual cycles, childbirth, and infertility. Some factors include:
- Early onset of menstruation (before age 12)
- Not having experienced childbirth
- Having the first child after 30
- Going through menopause after 50
- Never taking oral contraceptives
- Infertility, regardless of the use of fertility drugs
Hormone Replacement Therapy
In women who have not undergone a hysterectomy, hormone therapy using estrogen with a combination of progestin for more than five years significantly increases the risk of ovarian cancer. For women who have undergone a hysterectomy, using estrogen for more than ten years increases the risk.
Obesity
Those who consume a high-fat diet or have a BMI of 30 or more are at a higher risk of getting ovarian cancer.
References